A foundation piling system in which pilings are used to support a foundation system in soil having a varied composition and moisture content. The pilings extend into concrete grade beams forming a portion of a monolithic system including a concrete slab. Flanges extend from the end portions of the pilings that are disposed in the grade beam and a plurality of horizontally extending reinforcing bars extend through openings in the flanges.
If we wanna build houses or building, we need a basic foundation, obtain the tensile strength required, to survive handling and driving, and to provide sufficient bending resistance. Same goes in Health system, need a concrete and strong basic foundation to set up Hospital.
WHO’s definition of health system: “comprising all the organizations, institutions and resources that are devoted to producing health actions and include provision and consumption of traditional and complementary medicine (TCM) and Health awareness campaign.
Pillars/Subcomponents of hospital (WHO Indonesia)
1. Human Resources
According to WHO, the health workforce includes not only clinically trained health professionals but also nonclinical health management and support workers. They serve in both the public and private sectors. Each country has different workforce needs, which will have to be estimated while taking into consideration the limitations of range, skill mix, and demographics of the currently available workforce.
Pillars/Subcomponents of hospital (WHO Indonesia)
1. Human Resources
According to WHO, the health workforce includes not only clinically trained health professionals but also nonclinical health management and support workers. They serve in both the public and private sectors. Each country has different workforce needs, which will have to be estimated while taking into consideration the limitations of range, skill mix, and demographics of the currently available workforce.
Doctors, nurses, hospital attendants, technologists, clinical assistants and pharmacists are directly involved in providing OPD and ward care, administration, public relation, security, catering, laundry, electronics, civil, electrical and air conditioning maintenance are involved in supporting the former for providing safe health care. Planning needs to be done for all these personnel and not only for the direct caregivers.
How to improv it is by improving work system to get co-operation and collaboration among all employess, do employee education, training and development and also important to make employee satisfied
How to improv it is by improving work system to get co-operation and collaboration among all employess, do employee education, training and development and also important to make employee satisfied
Most Recommended Health Workforce Indicator
- WHO has found that minimum of 2.3 physician, nurses and midwives per 1 000 population are needed to meet 80% coverage of skilled bith attendance (SBA) and other research cite quite similar, 2.5 (Chen, et al. 2004: WHO, 2006a)
- Distribution of health workforce. the goal would be to decrease disparities in density per capita per X population across measurement units.
- Domestic education of healt proffesional
- indicator to monitor national workfirce management
2. Health Information System A combination of health statistics from various sources, used to derive information about health status, health care, provision and use of services and health impact Informatics Hospital information system. A system that provides information management features that hospitals need for daily business Features Pt tracking, billing and administrative programs; may include clinical features
3. Health Financing
According to WHO, the purpose of health financing is to “make funding available, as well as to set the right financial incentives to providers, to ensure that all individuals have access to effective public health and personal health care” (WHO, 2000). This building block is essential for the operation of a national health system – if financing were to fail, no health promotion or disease prevention would be able to take place.
Health financing refers not only to funds coming from the government but also to funds spent by individuals on their health care (out-of-pocket expenditures) and funds coming from and managed by the private sector, such as employers and insurers. In developing countries, additional funds come from donors and are either administered by donors themselves or given to the government or a private institution to be administered as they do their own funds. Donor funding is not a sustainable source of funding in the long term, so health system plans should include increasing domestic spending on health to eventually bridge the gap currently covered by donor funds. In the short term, increasing the diversity of international donors is important to protect against unexpected discontinuation of funds (WHO, 2007).
4. Health Information
A good information system has four main functions : to generate, compile, analyze and synthesize, and communicate and use health data, it aims to help in the decisionmaking process (WHO, 2008). Their main objective is to produce information for improved health services and evidence-based policy decisions that will lead to improvements in the health status of the population. Although they do not directly improve or reduce health status, reliable and timely health information is an essential foundation of public health action and health systems strengthening, both nationally and internationally. Information is therefore used as a management and oversight tool to improve outcomes through the analysis of changes in outcomes, as well as the processes and capacity being applied to achieve the outcomes (Perrin, et al., 1999).
5. Health Services delivery
WHO defines service delivery as the way inputs are combined to allow the delivery of a series of interventions or health actions (WHO, 2001a). Service delivery is the main function the health system has to perform, and it is often thought of as the only function of a health system. Service delivery is an immediate output of the inputs of the other building blocks, such as health workforce, medical products, and finances (Islam, 2007).
Measures of service delivery outputs include access, utilization, and coverage, which indicate whether people are receiving the services they need (WHO, 2008). Access includes a wide array of measures, including physical, financial, and sociopsychological access to services.
Most Recommended Service Delivery Indicators
Most Recommended Service Delivery Indicators
- the number and distribution of inpatient beds per 10 000 population is the single most mentioned indicator by major sources. there is no specific threshold for this indicator, generally a greater number of hospital beds suggest greater availability on inpatient health servicesnumber and distribution of health facilities per 10 000 population. ( actually only few benchmarks for this indicator)
- measuring basic service capacity based on an index of availability of basic amenities, basic equipment, infection control, health workers, and tracer drugs and diagnostics in a facility. The standard should be obtained directly from the MOH and may include standards or conditios other than equipment (e.g: material, electricity, running water and lab services)
- another basic service capacity indicator, more specific to a disease such as malaria conrol, Intergrated Management of childhood Illness(IMCI), safe motherhood, family planning, HIV/AIDS, control of sexually transmitted disease, TB control ot control of noncommunicable disease.
- Number of outpatient department(OPD) visits per 10 000 population per year.
- Quality of care
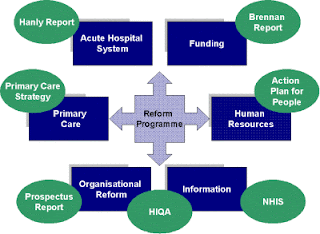
example health care crisis in for Irish Health Service :)

No comments:
Post a Comment